- Overview
- Guides
- Concepts
- Considerations And Constraints
- Absolute File References
- Assembly Colocation Assumptions
- Concurrent Use Of Test Resources
- Cross Application Domain Testing
- Heavily Executed Code Under Test
- Implicit File Dependencies
- Multi Threaded Tests
- Netstandard Test Projects
- Project Atomicity
- Project Build Platform And Configuration
- Rdi Data Point Location
- Test Atomicity
- Unique Test Names
- Using NCrunch With Source Control
- Reference
- Global Configuration
- Overview
- Auto Adjust Clashing Marker Colours
- Build Log Verbosity
- Build Process Memory Limit
- Capabilities Of This Computer
- Coverage Marker Style
- Cpu Cores Assigned To NCrunch Or Ide
- Custom Environment Variables
- Disable Global Hotkey
- Engine Hosting Strategy
- Fast Lane Threads
- Fast Lane Threshold
- Grid Maximum Reconnection Attempts
- Grid Reconnection Delay
- Impact Detection Mode
- Listening Port
- Log To Output Window
- Logging Verbosity
- Marker Colours
- Max Failing Test Trace Log Size
- Max Number Of Processing Threads
- Max Passing Test Trace Log Size
- Max Test Runners To Pool
- NCrunch Tool Window Colors
- Node Id (Name)
- Password
- Performance Aggregation Type
- Performance Display Sensitivity
- Pipeline Optimisation Priority
- Rdi Storage Settings
- Sliding Build Delay
- Snapshot Storage Directory
- Solution Storage Data Limit
- Spinner Colours
- Terminate Test Runners On Complete
- Test Process Memory Limit
- Tests To Execute On This Machine
- Text Output Font
- Workspace Base Path
- Solution Configuration
- Overview
- Additional Files For Grid Processing
- Additional Files To Include
- Allow Parallel Test Execution
- Allow Tests In Parallel With Themselves
- Infer Project References Using Assembly
- Instrumentation Mode
- NCrunch Cache Storage Path
- Only Consider Tests Outofdate If Impacted
- Project Config File Storage Path
- Show Coverage For Tests
- Show Metrics For Tests
- Tests To Execute Automatically
- Project Configuration
- Overview
- Additional Files To Include
- Allow Dynamic Code Contract Checks
- Allow Static Code Contract Checks
- Analyse Line Execution Times
- Autodetect Nuget Build Dependencies
- Build Priority
- Build Process Cpu Architecture
- Build Sdk
- Collect Control Flow During Execution
- Consider Inconclusive Tests As Passing
- Copied Project Dependencies
- Copy Referenced Assemblies To Workspace
- Custom Build Properties
- Data Storage File Size
- Default Test Timeout
- Detect Stack Overflow
- Enable Rdi
- Files Excluded From Auto Build
- Framework Utilisation Types
- Ignore This Component Completely
- Implicit Project Dependencies
- Include Static References In Workspace
- Instrument Output Assembly
- Method Data Limit
- Ms Test Thread Apartment State
- Preload Assembly References
- Prevent Signing Of Assembly
- Proxy Process File Path
- Rdi Cache Size
- Required Capabilities
- Restrict Tostring Usage
- Run Pre Or Post Build Events
- String Length Limit
- Track File Dependencies
- Use Build Configuration
- Use Build Platform
- Use Cpu Architecture
- Runtime Framework
- Overview
- Atomic Attribute
- Category Attribute
- Collect Control Flow Attribute
- Distribute By Capabilities
- Duplicate By Dimensions
- Enable Rdi Attribute
- Environment Class
- Exclusively Uses Attribute
- Inclusively Uses Attribute
- Isolated Attribute
- Method Data Limit Attribute
- Requires Capability Attribute
- Restrict Tostring Attribute
- Serial Attribute
- String Length Limit Attribute
- Timeout Attribute
- Uses Threads Attribute
- Global Configuration
- Troubleshooting
- Tools
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Manual Installation Instructions
Test Pipeline
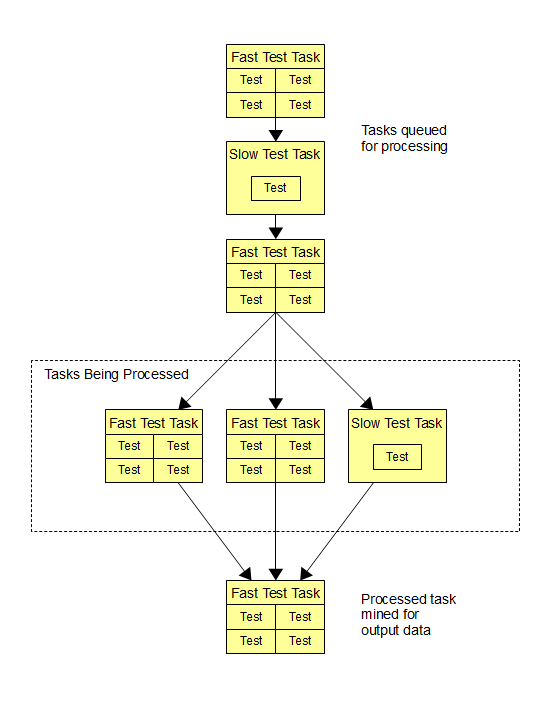
The Test Pipeline is a conceptual term used to describe the behaviour of NCrunch's engine when it executes tests fed to it from the build output. The pipeline itself consists of a series of prioritised tasks containing physical groups of tests.
The logic used to group the tests into tasks takes into consideration a number of factors, including:
- Length of test execution
- Distribution of tests between their parent fixtures
- Length of fixture setup and teardown
- Resource requirements (as controlled by ExclusivelyUsesAttribute, InclusivelyUsesAttribute and SerialAttribute)
- Framework type (NUnit, MSpec, etc)
- Priority
The engine will use this information to try to construct a pipeline that will give the most relevant feedback within the shortest possible time. Prioritisation of these tasks will also take into consideration changes that you have recently made to your codebase - as impacted tests are considered much higher value than others.
It should be noted that it is physically possible for a test to exist in the pipeline multiple times. This is because the engine can be executing multiple versions of your source code at any one time, and therefore a test can actually be running concurrently with another version of itself. This behaviour is configurable.
Data returned from tests after their execution (such as status and code coverage) will be batched together and will only be returned in bulk when the entire task finishes executing. The engine takes this into consideration when building the pipeline and ensures that large and long running tests are placed into their own distinctive tasks to avoiding holding up any other badly needed information.
While you work through your codebase, the test pipeline will be in a constant state of flux. The engine will not interrupt tests while they are partway executing, but it will regularly clear out pending test tasks from the pipeline when new data becomes available from builds. The processing queue window gives a good physical view of the test pipeline along with the status of the work and priorities etc. It can sometimes be useful to work with this view open so as to have some information about the progress of the engine.
Because the engine can theoretically pipeline tests in any grouping or order, you should take care to write high quality tests that do not make dangerous assumptions about their execution order or the state of their application domain.
To ensure the processing queue is not obstructed, NCrunch will rigorously enforce test timeouts.